Full Post
For paid subscribers:
Full video essay of the post
Lots of summary tables with main information from post
Additional resources mentioned in video essay
Google Doc link to the full post for use with LLMs
Learn about optical transceiver names in 5 minutes and bore your family to sleep even before the turkey sets in!
Happy Thanksgiving!
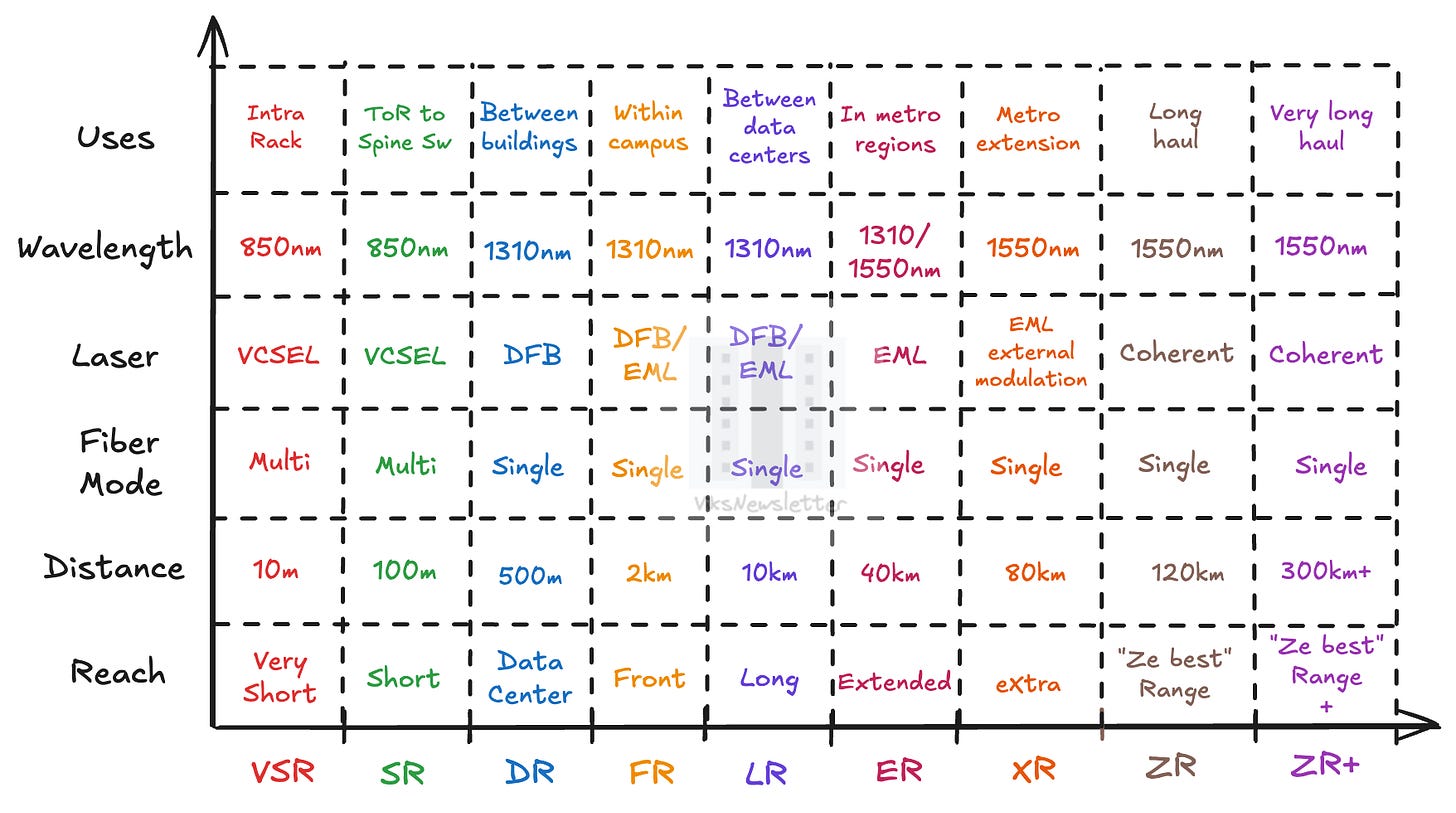
Optical Transceiver Nomenclature in a Single Image
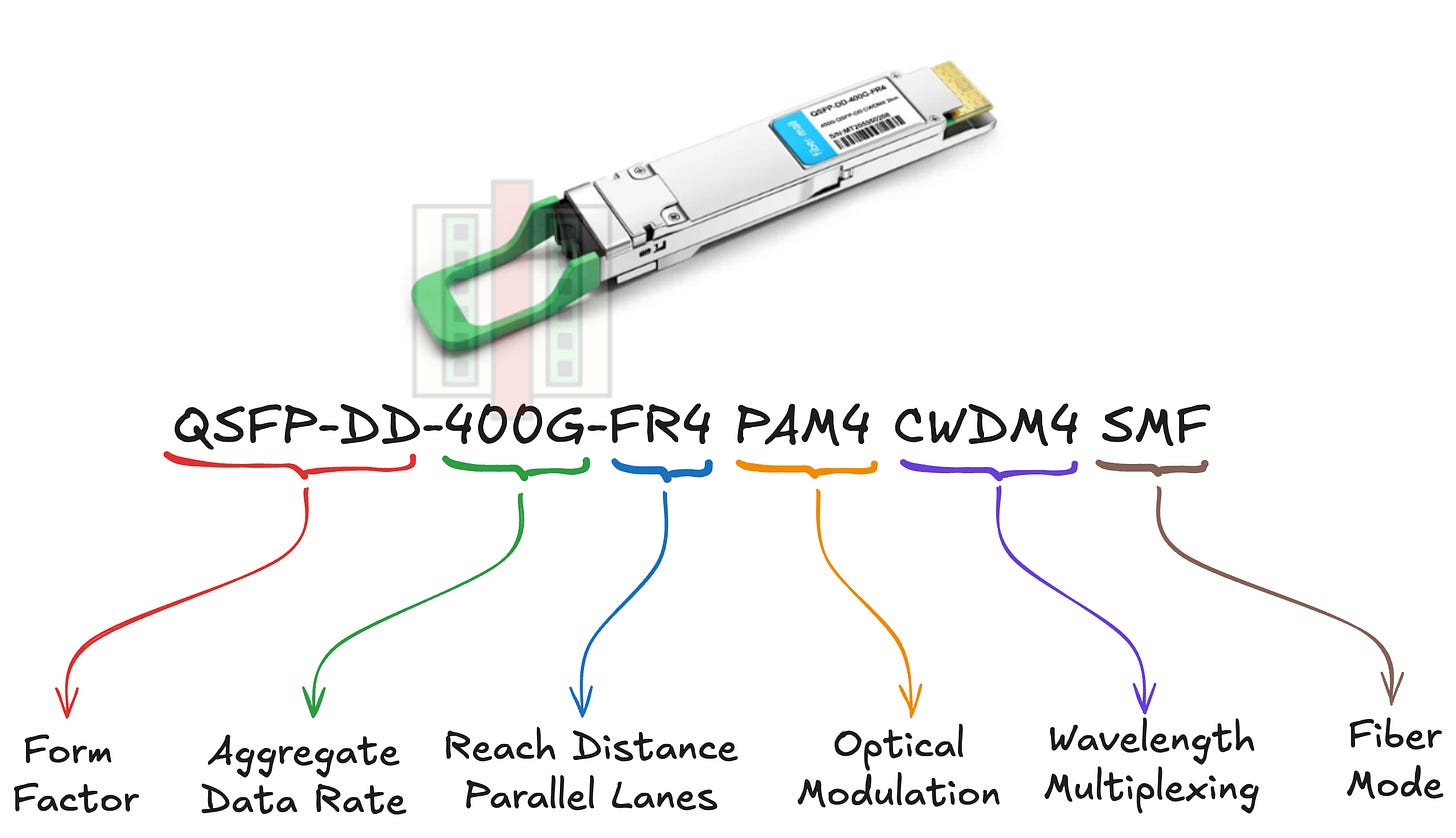
Quick Decode Example
QSFP-DD-400G-FR4 PAM4 CWDM4 SMF
QSFP-DD: 8-lane double-density pluggable
400G: 400 Gbps aggregate
FR4: Front reach (~2km), 4 dual-lanes, 2×50G per lane
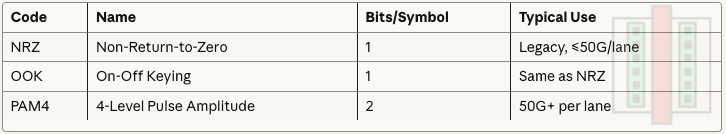
PAM4: 4-level pulse amplitude modulation via:
Direct laser modulation, or
CW laser + external modulator using:
Electro-absorption modulator (EAM) → adjustable laser absorption levels
Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) → adjustable interference
Ring modulator → adjustable resonance
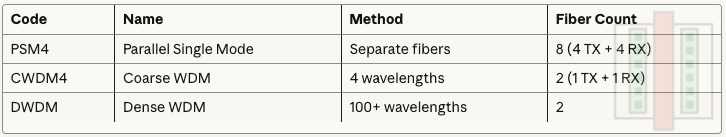
CWDM4: 4 wavelengths used for coarse wavelength division multiplexing
1271/1291/1311/1331nm
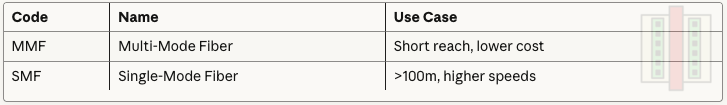
SMF: Single-mode fiber
Translation: A mainstream 400G module for building-to-building datacenter links.
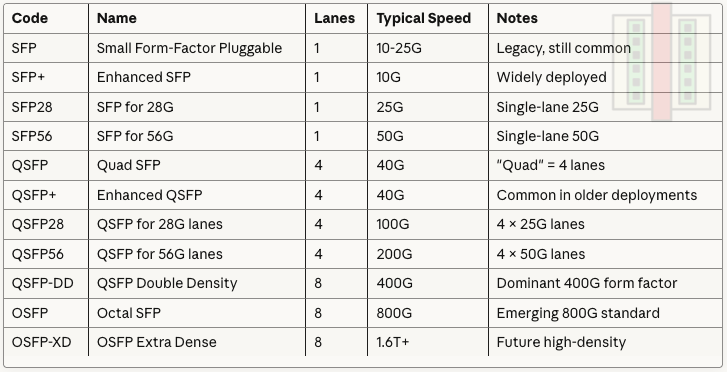
Form Factor
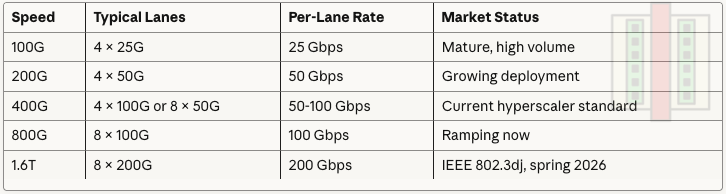
Aggregate Data Rate
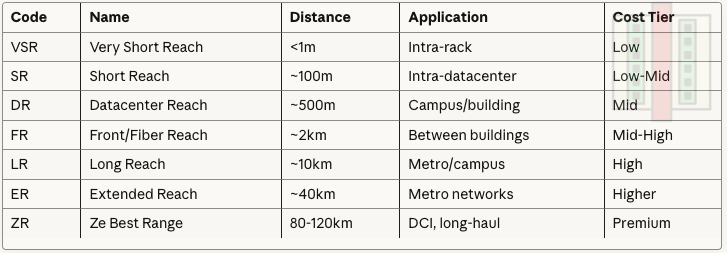
Reach Distance
Modulation
Direct Modulation → Adjust the drive current to laser diode and generate different laser output levels for modulation.
External Modulation → Keep laser power constant, and use an external modulator to get different laser output levels.
Electro-Absorption Modulators → Voltage applied causes different levels of absorption of laser light; produces different output levels.
Mach-Zehnder Modulators → Uses principles of constructive/destructive interference to generate different levels of laser light at output.
Ring Modulators → Uses micro-rings to trap light wavelengths with resonance; applied voltage shifts resonance frequency and hence laser light output.
Multiplexing
Fiber Mode
All-in-One View of Optical Transceivers
Final Remark
Optical transceivers will still be relevant when co-packaged optics (CPO) arrives on the scene. There is no substitute for high bandwidth, long distance communications. The optical transceiver industry has a lot of moving parts: lasers, detectors, modulators, fiber, connectors, cooling, and a lot more. As we transition to higher data rates, the design of all of these components gets challenging.
There are an great number of companies out there working on interesting optics related problems - all of which I cannot cover in this post. However, I will be keeping a close watch about developments in the optical world in this newsletter.
Additional Resources
Understanding the Duplex LC Connector: The Go-To Fiber Network Solution
400G ZR, DR4, FR4, LR4, SR8 QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Overview